Goiânia accident
The Goiânia accident was a radioactive contamination accident that occurred on September 13, 1987, at Goiânia, in the Brazilian State of Goiás after an old radiotherapy source was taken from an abandoned hospital site in the city. It was subsequently handled by many people, resulting in four deaths and radioactive contamination of 245 other people, 20 of whom showed signs of radiation sickness and required treatment.[1][2] Time magazine has identified the accident as one of the world's "worst nuclear disasters".[3]
Contents |
Nature of the source
The source of the Goiânia accident was a small thimble containing about 93 grams of highly radioactive caesium chloride (a caesium salt made with a radioisotope, caesium-137) encased in a shielding canister made of lead and steel with an iridium window. The source was positioned in a container of the wheel type, where the wheel turns inside the casing to move the source between the storage and irradiation positions.[4]
| Goiânia source | TBq |
|---|---|
| 1971 | 74 |
| 1987 | 50.9 |
| Recovered | 44 |
| Unrecovered (c. 1987) | 7 |
| Unrecovered (c. 2012) | 3.9 |
| Smoke detector | 0.000000037 |
The source emitted 74 terabecquerels (TBq) in 1971. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) describes the container—51 millimeters (2 inches) in diameter and 48 mm (1.8 inches) long—as an “international standard capsule.” The specific activity of the active solid was about 814 TBq·kg−1 of caesium 137 (half life of 30 years). The dose rate at one meter from the source was 4.56 gray per hour (456 rad·hr−1). While the serial number of the device was unknown, thus hindering definitive identification, the device was thought to be made in the United States at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and was used as a radiation source for radiation therapy at the Goiânia hospital.[4]
The IAEA document indicates that:
- The dose rate due to external irradiation from uniform contamination of the ground by 137Cs is
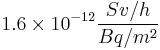
- The internal dose for ingestion is
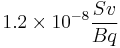
- The internal dose for inhalation is
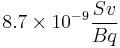
The IAEA states that the source contained 50.9 TBq (1375 Ci) when it was taken and that about 44 TBq (1200 Ci, 87%) of radioactivity has been recovered during the clean up operation. This means that 7 TBq remained in the environment; it will have decayed to about 3.9 TBq by 2012.
For comparison, the average modern smoke detector contains about 37 kBq (1 μCi) of 241Am.[5]
Events
Hospital abandonment
The Instituto Goiano de Radioterapia (IGR), a private radiotherapy institute in Goiânia,[4] was located just 1 km (0.62 mi) northwest of Praça Cívica, the administrative center of the city. It moved to its new premises in 1985, leaving behind a caesium-137 based teletherapy unit which had been purchased in 1977. The fate of the abandoned site was disputed in court between IGR and the Society of Saint Vincent de Paul, then owner of the premises.[6] On 11 September 1986, the Court of Goiás stated it had knowledge of the abandoned radiological material in the building.[6]
Four months prior to the accident, on 4 May 1987, Saura Taniguti, then director of Ipasgo, the institute of insurance for civil servants, used police force to prevent one of the owners of IGR, Carlos Figueiredo Bezerril, from removing the objects that were left behind.[6] Bezerril then warned president of Ipasgo, Lício Teixeira Borges, that he should take responsibility "for what would happen with the caesium bomb".[6]
The court posted a security guard to protect the hazardous abandoned equipment.[7] Meanwhile, the owners of IGR wrote several letters to the National Commission for Nuclear Energy, warning them about the danger of keeping a teletherapy unit at an abandoned site, but they could not remove the equipment by themselves once a court order prevented them from doing so.[6][7]
Theft of the source
On 13 September 1987, the security guard in charge of daytime security, Voudireinão da Silva, did not show up to work, using a sick day to attend a cinema screening of Herbie Goes Bananas with his family.[7] That same day, scavengers Roberto dos Santos Alves and Wagner Mota Pereira entered the partially demolished facility, found the teletherapy unit, which they thought might have some scrap value, placed it in a wheelbarrow, and took it to Alves' home,[8] about 0.6 km north of the clinic. There, they partly dismantled the equipment, taking the billiard ball-sized caesium capsule out of the protective rotating head. The gamma radiation emitted by the capsule's iridium window nauseated the men, and within a day or so, the two men became ill, experiencing vomiting, diarrhea, and dizziness. The clinic's diagnosis was that the men were suffering an allergic reaction caused by eating bad food.[1] The two continued their efforts to dismantle the unit, eventually rupturing the source capsule and exposing the radioactive material. The exposure eventually caused localized burns to their bodies, and one later had to have an arm amputated.
The source is partially broken
A few days later one man broke open the iridium window, which allowed him to see the caesium chloride emitting a deep blue light.[1]
The exact mechanism by which the light was generated was not known at the time the IAEA report was written. The light is thought to be either fluorescence or Cherenkov radiation associated with the absorption of moisture by the source; similar blue light was observed in 1988 at Oak Ridge National Laboratory during the disencapsulation of a 137Cs source. The man scooped out some of the radioactive caesium and tried to light it, thinking it was gunpowder, and eventually gave up.
The source is sold and dismantled
On September 18, Roberto dos Santos Alves and Wagner Mota Pereira sold the items to a nearby scrapyard. That night the owner, Devair Alves Ferreira, went in the garage and saw the blue glow from the caesium capsule. Over the next three days, he invited friends and family to view the strange glowing substance. Ferreira intended to make a ring for his wife, Gabriela Maria Ferreira, out of the material.
Several people who visited the home came into contact with the dust and spread it around the local neighborhood and to other towns nearby. Ferreira's ownership led to many people becoming contaminated. A brother of the scrapyard owner used the dust to paint a blue cross on his abdomen. He also contaminated the animals at his farm, several of which died. At this scrapyard, a friend of Ferreira's (given as EF1 in the IAEA report) hammered open the lead casing. On 25 September 1987, Devair Alves Ferreira sold the scrap metal to another scrapyard. He survived the incident.
Ivo and his daughter
Ivo, Devair's brother, scraped dust out of the source, taking it to his house a short distance away. There he spread some of it on the floor. His 6-year-old daughter, Leide das Neves Ferreira, later ate while sitting on the floor, absorbing some of the radioactive material (1.0 GBq, total dose 6.0 Gy). She was also fascinated by the blue glow of the powder, applied it to her body and showed it off to her mother.
Gabriela Ferreira notifies authorities
Gabriela Maria Ferreira was the first to notice that many people around her had become severely sick all at the same time, and her actions from that point on probably saved lives. She first suspected the culprit was a beverage they had shared, but an analysis of the juice showed nothing untoward. On 28 September 1987 (15 days after the item was found), Gabriela went with one of her scrapyard employees to the scrapyard then in possession of the materials. She reclaimed them and transported them by bus in a plastic bag to a hospital. There, physician Paulo Roberto Monteiro rightly suspected that it was dangerous. He placed it in his garden on a chair to increase the distance between himself and the object. Because the remains of the source were kept in a plastic bag, the level of contamination at the hospital was low.
The source's radioactivity is detected
In the morning of 29 September 1987 a visiting medical physicist (named WF in the IAEA report) used a scintillation counter borrowed from NUCLEBRAS (a national government agency which is involved in the nuclear fuel cycle, including searching for uranium ore) to confirm the presence of radioactivity. He spent most of the day on 29 September confirming the danger and persuading the authorities to take immediate action. The city, state, and national governments were all aware of the incident by the end of the day, and the accident response started that evening.
Health outcomes
About 130,000 people overwhelmed hospitals.[2] Of those, 250 people, some with radioactive residue still on their skin, were found, through the use of Geiger counters, to be contaminated.[2] Eventually, 20 people showed signs of radiation sickness and required treatment.[2]
Ages in years are given, with dosages listed in Gy, or Gray.
Fatalities
- Leide das Neves Ferreira, aged 6 (6.0 Gy, 600 REM), was the daughter of Ivo Ferreira. Initially, when an international team arrived to treat her, she was confined to an isolated room in the hospital because the hospital staff were afraid to go near her. She gradually developed swelling in the upper body, hair loss, kidney and lung damage, and internal bleeding. She died on October 23, 1987, of "septicemia and generalized infection" at the Marcilio Dias Navy Hospital, in Rio de Janeiro, as a result of the contamination.[2] She was buried in a common cemetery in Goiania, in a special fiberglass coffin lined with lead to prevent the spread of radiation.[2] There was a riot in the cemetery, where over 2,000 people armed with stones and bricks tried to prevent her burial.[9]
- Gabriela Maria Ferreira, aged 38 (5.7 Gy, 550 REM), wife of junkyard owner Devair Ferreira, became sick about three days after coming into contact with the substance. Her condition worsened, and she developed internal bleeding, especially in the limbs, eyes, and digestive tract, and suffered from hair loss. She died 23 October 1987, about a month after exposure.
- Israel Baptista dos Santos, aged 22 (4.5 Gy, 450 REM), was an employee of Devair Ferreira who worked on the radioactive source primarily to extract the lead. He developed serious respiratory and lymphatic complications, was eventually admitted to hospital, and died 6 days later on 27 October 1987.
- Admilson Alves de Souza, aged 18 (5.3 Gy, 500 REM), was also an employee of Devair Ferreira who worked on the radioactive source. He developed lung damage, internal bleeding, and heart damage, and died 18 October 1987.
Devair Ferreira himself survived despite receiving 7 Gy of radiation.
Other individuals
The outcomes for the 46 most contaminated people are shown in the bar chart below. Several people survived high doses of radiation. This is thought in some cases to be because the dose was fractionated. Given time, the body's repair mechanisms will reverse cell damage caused by radiation. If the dose is spread over a long time period, these mechanisms can ameliorate the effects of radiation poisoning.
Other affected persons
Afterwards, about 112,000 people were examined for radioactive contamination; 249 were found to have significant levels of radioactive material in or on their body.[1] Of this group, 129 persons had internal contamination. The majority of the internally contaminated persons only suffered small doses (< 50 mSv, less than a 1 in 400 risk of getting cancer as a result).
A thousand persons were identified as having suffered a dose which was greater than one year of background radiation; it is thought that 97% of these people had a dose of between 10 and 200 mSv (between 1 in 2 000 and 1 in 100 risk of developing cancer as a result).
Legal matters
In light of the deaths caused, the three doctors who had owned and run IGR were charged with criminal negligence. The main cause of this incident was the severe negligence of the facility's former operators who had left behind such a dangerous item. The accident demonstrated the importance of keeping an inventory and monitoring of all strong radiation sources by public authorities, which now is legally required in many countries. In 2000, CNEN, the National Nuclear Energy Commission, was ordered by the 8th Federal Court of Goiás to pay compensation of R$ 1.3 million and to guarantee medical and psychological treatment for the direct and indirect victims of the accident and their descendants down to the third generation.[10] Because the accidents occurred before the promulgation of the Federal Constitution of 1988 and because the substance was acquired by the clinic and not by the individual owners, the court could not declare the owners of IGR liable. One of the medical doctors owning IGR and the clinic's physicist were ordered to pay R$ 100 000 for the derelict condition of the building. The two scrap metal dealers were not included as defendants in the public civil suit.
Cleanup
Objects and places
Topsoil had to be removed from several sites, and several houses were demolished. All the objects from within those houses were removed and examined. Those that were found to be free of radioactivity were wrapped in plastic bags, while those that were contaminated were either decontaminated or disposed of as waste. In industry, the choice between decontaminating or disposing objects is based only on the economic value of the object and the ease of decontamination. However, in this case, the IAEA recognized that to reduce the psychological impact of the event, greater effort should be taken to clean up items of personal value, such as jewelry and photographs. It is not clear from the IAEA report to what degree this was practiced.
Means and methods
After the houses were emptied, vacuum cleaners were used to remove dust before the surfaces, and plumbing was examined for radioactivity. Painted surfaces could be scraped, while floors were treated with acid and Prussian blue mixtures. Roofs were vacuumed and hosed, but two houses had to have their roofs removed. The waste from the clean up was moved out of the city to a remote place for storage.
Potassium alum dissolved in hydrochloric acid was used on clay, cement, soil, and roofs. Caesium has a high affinity for many clays.
Organic solvents, followed by potassium alum dissolved in hydrochloric acid, were used to treat waxed/greased floors and tables. Sodium hydroxide solutions, also followed by dissolved potassium alum, were used to treat synthetic floors, machines and typewriters.
Prussian blue was used to internally decontaminate many humans. The urine was treated with ion exchange resin to compact the waste for ease of storage.
Recovery considerations
The cleanup operation was much harder for this event than it could have been because the source was opened, and the fact that the active material was water soluble. A sealed source need only be picked up, placed in a lead container and transported to the radioactive waste storage. In the recovery of lost sources, the IAEA recommends careful planning and using a crane or other device to place shielding (such as pallet of bricks or a concrete block) near the source to protect recovery workers.
Contamination locations
The Goiânia accident spread significant radioactive contamination throughout the Aeroporto, Central, and Ferroviários districts. Even after the cleanup, 7 TBq of radioactivity remained unaccounted for.
Some of the key contamination sites:
- Goiânia’s Instituto Goiano de Radioterapia (IGR) ()[1] suffered no actual exposure or breach of radioactive contents, but the site is noteworthy as the source of deadly, unsecured material. The IGR clinic no longer exists, having been replaced around 2000 with the modernized Centro de Convenções convention center.
- Roberto dos Santos' house ()[1] on Rua 57. The radioactive source was here for about six days, and it was partially broken into.
- Devair Ferreira's scrapyard (),[1] on Rua 15A ("Junkyard I") in the Aeroporto section of the city, had possession of the items for 7 days. The caesium container was entirely dismantled, spreading significant contamination. Extreme radiation levels of up to 1.5 Sv h−1 were found by investigators in the middle of the scrapyard.
- Ivo Ferreira's house ()[1] ("Junkyard II"), at 1F Rua 6. Some of the contamination was spread about the house, causing a fatality. The adjacent junkyard scavenged the remainder of parts from the IGR facility. The premises were contaminated with up to 2 Sv h−1 of detectable radiation.
- Junkyard III ().[1] This junkyard had possession of the items for 3 days until they were sent away.
- Vigilância Sanitária ().[1] Here, the substance was quarantined, and an official cleanup response began.
Research
In 1991, a group of researchers collected blood samples from highly-exposed survivors of the incident. Subsequent analysis resulted in the publication of numerous scientific articles.[11][12][13][14]
See also
- List of civilian radiation accidents
- Lists of nuclear disasters and radioactive incidents
- Three Mile Island accident
- Chernobyl disaster
- Windscale fire
- Nuclear and radiation accidents
- Radioactive waste
- Mayapuri radiological accident in Delhi
- Radiotherapy accident in Zaragoza
- Radiotherapy accident in Costa Rica
- Orphan source
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j The Radiological Accident in Goiania, IAEA, 1988
- ^ a b c d e f Foderaro, Lisa. "Columbia Scientists Prepare for a Threat: A Dirty Bomb". The New York Times. July 8, 2010.
- ^ The Worst Nuclear Disasters
- ^ a b c The Radiological Accident in Goiânia. IAEA. 1988-09-16. ISBN 92-0-129088-8. http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PubDetAR.asp?pubId=3684.
- ^ "Smoke Detectors & Radiation". United States Environmental Protection Agency. http://www.epa.gov/radiation/sources/smoke_alarm.html. Retrieved 2007-11-04.
- ^ a b c d e (Portuguese) Godinho, Iúri. "Os médicos e o acidente radioativo". Jornal Opção. February 8, 2004.
- ^ a b c (Portuguese) Borges, Weber. "O jornalista que foi vítima do césio". Jornal Opção. May 27, 2007.
- ^ Mamchur, Fedoska. "This Date in History – September 13, 1987". SafetyXchange. September 13, 2007.
- ^ (Portuguese) "Memorial Césio 137". Greenpeace Brasil.
- ^ (PDF) Case Law and Administrative Decisions, Judgement of the Federal Court in the Public Civil Action concerning the Goiânia Accident, OECD, 2000, http://www.oecd-nea.org/law/nlb/Nlb-66/023-032.pdf.
- ^ Da Cruz, AD; Curry, J; Curado, MP; Glickman, BW (1996). "Monitoring hprt mutant frequency over time in T-lymphocytes of people accidentally exposed to high doses of ionizing radiation". Environmental and molecular mutagenesis 27 (3): 165–75. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(1996)27:3<165::AID-EM1>3.0.CO;2-E. PMID 8625952.
- ^ Saddi, V; Curry, J; Nohturfft, A; Kusser, W; Glickman, BW (1996). "Increased hprt mutant frequencies in Brazilian children accidentally exposed to ionizing radiation". Environmental and molecular mutagenesis 28 (3): 267–75. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(1996)28:3<267::AID-EM11>3.0.CO;2-D. PMID 8908186.
- ^ Da Cruz, AD; Volpe, JP; Saddi, V; Curry, J; Curadoc, MP; Glickman, BW (1997). "Radiation risk estimation in human populations: lessons from the radiological accident in Brazil". Mutation research 373 (2): 207–14. PMID 9042402.
- ^ Skandalis, A; Da Cruz, AD; Curry, J; Nohturfft, A; Curado, MP; Glickman, BW (1997). "Molecular analysis of T-lymphocyte HPRT– mutations in individuals exposed to ionizing radiation in Goiânia, Brazil". Environmental and molecular mutagenesis 29 (2): 107–16. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(1997)29:2<107::AID-EM1>3.0.CO;2-B. PMID 9118962.